Machine Learning: Real-Time Traffic Sign Detecton
My theses project using Python (Yolov8s & Resnet50V2) to create a Real-Time Traffic Sign Detecton System.
Quick Description
This thesis project was completed during my third and fourth year in the Computer Science program. The study focuses on developing a real-time traffic sign recognition system using a hybrid algorithm that combines YOLOv8s for detection and ResNet50V2 for classification. The system is designed to run inside a vehicle using a mini computer powered directly by the car, and it functions entirely without the need for internet access. A standard 720p webcam is used to capture the video feed for processing. For output, the mini computer acts as a hotspot that allows multiple devices to connect and view the system’s results through a web-based interface.
Images & Videos
The promotional video used during the presention of our thesis
Website preview on an emulated android viewport 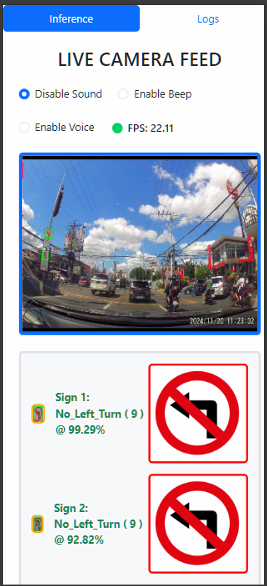
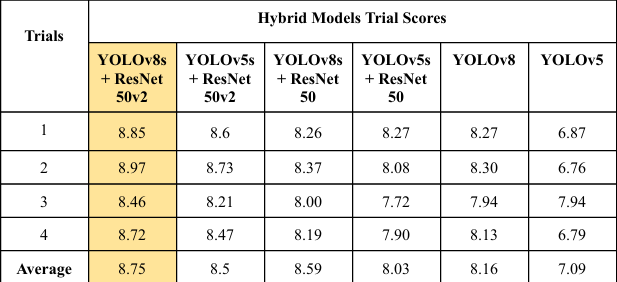
Trial Scores of different algorithm using our dataset.
In Depth View: The following parts will contain parts or summaries of what we wrote in the actual paper. For the actual paper click here
Abstract
Disregarding traffic signs often lead to accidents or apprehensions. Developing a system that can detect and classify traffic signs in real-time can help significantly in adhering to traffic signs to reduce accidents and apprehension. However, research on the implementation for the real-time aspect of traffic sign detection and classification systems are limited. The main objective of this study was to develop a real-time traffic sign detection and classification system using YOLOv8s for detection and ResNet50V2 for classification. The data used in the study was collected from online sources. The results show that the hybrid implementation of YOLOv8s for detection and ResNet50V2 for classification effectively achieved high performance without compatibility issues. The integrated system reached an overall accuracy of 82.80%, thereby validating the effectiveness of the hybrid model in real-time traffic sign classification and detection tasks. The results of the study contributes to the field of computer vision by demonstrating the effectiveness of combining detection and classification architectures, potentially guiding future research in hybrid model design. Practically, the findings of the study can be applied to enhance existing systems used in autonomous vehicles.
Methodology
The hybrid YOLOv8–ResNet50V2 traffic sign recognition (TSR) algorithm first performs object detection using YOLOv8. YOLOv8 identifies potential traffic signs by generating bounding boxes that include coordinates and a confidence score. Only detections with at least 0.7 confidence are kept to reduce false positives. For each valid detection, the algorithm extracts the region of interest (ROI) and resizes it to 224×224 pixels, the required input size for ResNet50V2.
ResNet50V2 then classifies the extracted ROIs into categories such as speed limit, stop, or caution signs. Using a Softmax layer, it computes class probabilities and outputs the label with the highest score. This detection–classification pipeline runs in a real-time loop: YOLOv8 detects signs at 30 FPS, and ResNet50V2 classifies them with minimal delay. The final output, including bounding boxes and predicted labels, is displayed on the user interface.
Summary and Conclusion
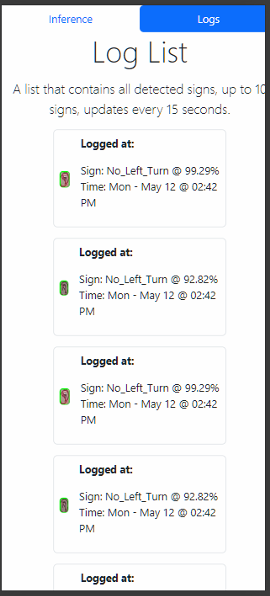
The study developed and evaluated a real-time traffic sign detection and classification system using a hybrid approach: YOLOv8s for object detection and ResNet50V2 for image classification. The system processes live video from a webcam, detects traffic signs, classifies them, and displays outputs through a mobile device connected to the same local network. An activity log records all detection events.
Separate datasets were used to train both models. YOLOv8s was trained on a synthetic dataset combining TT100K and ResNet images, while ResNet50V2 was trained on various consolidated datasets from Roboflow. YOLO was trained for 30 epochs with fine-tuning, and ResNet50V2 for 15 epochs with additional fine-tuning after unfreezing layers.
Real-time testing on a Mini PC recorded 279 detection events, achieving 82.80% accuracy in hybrid system performance. A broader evaluation using ISO/IEC 25010 standards, involving 25 IT and 25 non-IT professionals, showed strong positive feedback across Functional Suitability, Performance Efficiency, Reliability, Usability, and Compatibility. IT professionals rated Performance Efficiency highest (4.49), while non-IT professionals rated Usability highest (4.11).
In the conclusion, the system demonstrated strong real-time performance with 88.32% average accuracy, 91% precision, 88% recall/F1-score, ~30 FPS processing speed, and 1310 MB memory usage. However, accuracy decreases in low-light conditions and when encountering unfamiliar or non-English signs, indicating a need for dataset expansion and multilingual support.
Overall, the system met its research objectives, proving effective, robust, and user-accepted for real-time traffic sign detection and classification.